- Understanding Startup Scouting
- The Startup Scouting Process
- Advanced Evaluation Criteria
- Managing Networks and Collaboration
- Tools and Software for Startup Scouting
- Challenges in Startup Scouting and Solutions
- Future Trends Impacting Startup Scouting
- Strategies for Different Stakeholders
- The Next Steps
- Key Takeaways
Technological advancements are accelerating, and markets are more competitive than ever. Staying ahead requires more than internal development—it demands engagement with the dynamic ecosystem of startups.
These early-stage companies often lead innovation, offering fresh ideas, novel technologies, and unique business models that can transform industries.
But what exactly is startup scouting, and how can organizations adopt this practice effectively?
This comprehensive guide explores the fundamentals of startup scouting, advanced strategies, and provides practical insights to navigate this area successfully.
If you're a corporate innovation manager seeking ways to integrate startups into your strategy, this article has you covered. It’s also tailored for venture capitalists searching for high-potential investments and looking to refine their approach.

For a deeper dive into the foundational concepts of startup engagement, explore our Comprehensive Startup Engagement Guide.
Understanding Startup Scouting
What Is Startup Scouting?
Startup scouting is the systematic process of identifying, evaluating, and engaging with early-stage companies that have the potential to drive innovation and provide strategic value.
It involves actively searching for startups that align with an organization's objectives. The process includes assessing their potential and evaluating their strengths.
It also focuses on building relationships with these startups. These connections can eventually lead to partnerships, investments, or acquisitions.
This practice includes various activities:
- Market Research: Keeping up with industry trends, emerging technologies, and innovative business models.
- Networking: Building relationships with entrepreneurs, incubators, accelerators, and other stakeholders in the startup ecosystem.
- Evaluation: Analyzing startups based on criteria such as product fit, market potential, team capabilities, and financial health.
- Engagement: Exploring collaboration opportunities through partnerships, investments, or pilot projects.
The Importance of Startup Scouting
Driving Innovation
As innovation cycles shorten, organizations need to grow and adapt continuously to stay competitive. Startup scouting enables companies to:
- Access Cutting-Edge Technologies: Engage with startups developing breakthrough technologies that can enhance or redefine existing markets.
- Incorporate Fresh Ideas: Infuse new thinking and creativity into their organization by collaborating with innovative startups.
- Accelerate Time to Market: Use startups' agility to bring new products or services to market faster.
Gaining a Competitive Edge
Early engagement with promising startups can provide:
- First-Mover Advantage: Exclusive access to innovative solutions before competitors.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborative relationships that strengthen market position and open new revenue streams.
- Market Intelligence: Insights into emerging market trends and customer needs.
Investing in Growth
For investors and corporations alike, identifying high-potential startups offers:
- Lucrative Investment Opportunities: Potential for significant returns as startups scale.
- Portfolio Diversification: Exposure to new industries and technologies.
- Long-Term Value Creation: Building relationships that can evolve into mergers, acquisitions, or long-term partnerships.
Investor Psychology in Startup Scouting
Understanding the human elements influencing investment decisions enhances the effectiveness of startup scouting. Investor psychology involves recognizing cognitive biases and behavioral patterns that can impact judgment.
Common Cognitive Biases
- Confirmation Bias: Seeking information that confirms preexisting beliefs while ignoring contradictory evidence.
- Overconfidence Bias: Overestimating one's ability to predict outcomes, leading to underestimated risks.
- Availability Heuristic: Relying on immediate examples that come to mind, which may not represent the broader reality.
- Herd Mentality: Following the crowd without independent analysis, potentially leading to overvaluation of certain startups.
Mitigating Biases in Decision-Making
- Diverse Perspectives: Involve a team with varied backgrounds to provide balanced viewpoints.
- Structured Evaluation Frameworks: Implement standardized criteria to reduce subjective judgments.
- Continuous Learning: Stay informed about psychological biases through training and reflection.
By addressing these psychological factors, investors can make more objective decisions, enhancing the success rate of their scouting efforts.
Learn about tailoring strategies to mitigate biases in our Tailored Scouting Strategies for Investors.
The Startup Scouting Process
How Do You Scout a Startup?
Effective startup scouting involves a structured approach to ensure comprehensive coverage and thorough evaluation. Here's a detailed step-by-step guide:
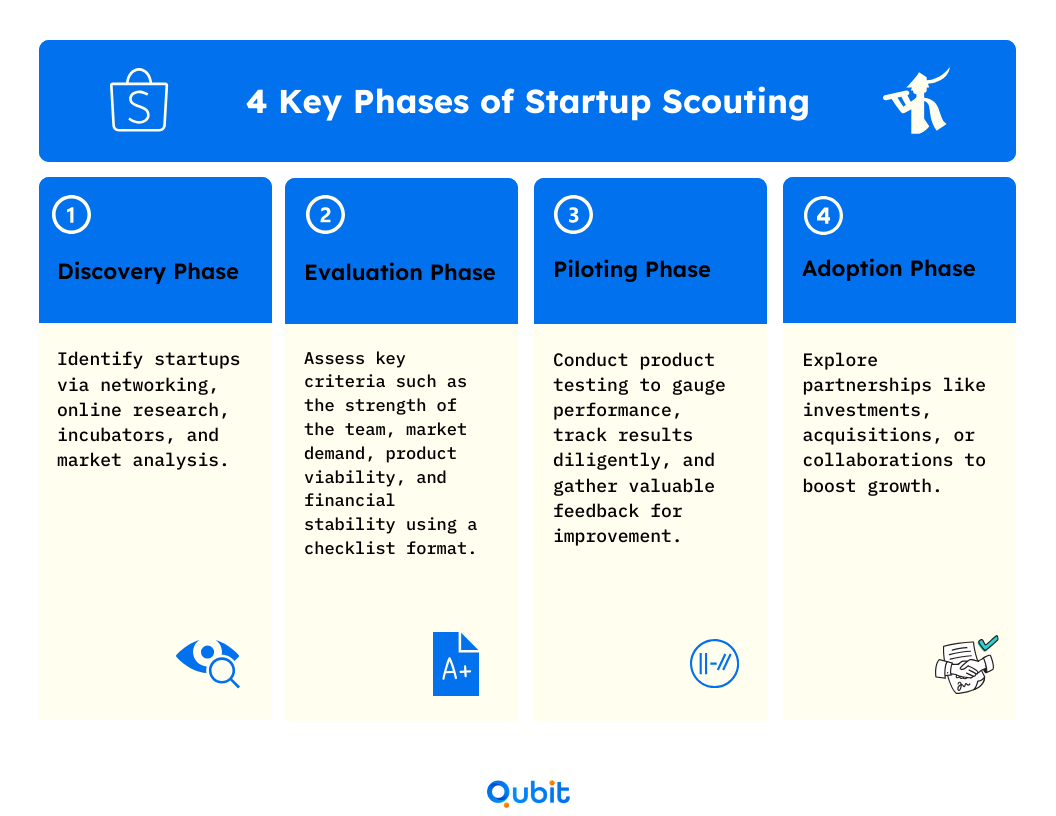
1. Discovery Phase
Objective: Identify potential startups that align with organizational goals.
Methods:
- Networking Events: Attend industry conferences, startup meetups, hackathons, and pitch events to connect with entrepreneurs.
- Online Platforms: Use databases and platforms to research startups.
- Incubators and Accelerators: Partner with these organizations to access curated batches of startups.
- Academic Institutions: Collaborate with universities and research institutions where innovation often originates.
- Industry Publications: Stay updated through journals, blogs, and news outlets covering emerging startups and technologies.
Pro Tip: Create a diverse pipeline by exploring both traditional sources and unconventional channels, such as social media groups or niche industry forums.
2. Evaluation Phase
Objective: Assess identified startups to determine their fit and potential.
Criteria:
- Alignment with Objectives: Determine how the startup's product or service aligns with your strategic goals.
- Team Capabilities: Evaluate the founders’ experience, expertise, and track record.
- Market Potential: Analyze the target market size, growth trajectory, and competitive landscape.
- Product Viability: Assess the technical feasibility, uniqueness, and value proposition.
- Financial Health: Review financial statements, funding history, and revenue models.
- Risk Assessment: Identify potential risks, including market entry barriers, regulatory challenges, and technological obsolescence.
Tools:
- SWOT Analysis: Identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Due Diligence Checklists: Systematically review all critical aspects of the startup.
Downloadable Resource: Access this Startup Evaluation Framework for a comprehensive checklist.
3. Piloting Phase
Objective: Test the startup's solution in a controlled environment to validate its effectiveness.
Steps:
- Define Pilot Objectives: Establish clear goals and success metrics.
- Set Up Environment: Create a controlled setting within your organization to implement the solution.
- Monitor Performance: Track key performance indicators (KPIs) related to usability, efficiency, and impact.
- Collect Feedback: Gather input from stakeholders and end-users.
- Adjust and Iterate: Work with the startup to refine the solution based on feedback.
Case Example:
A multinational retail corporation partnered with a startup offering AI-driven inventory management. By piloting the solution in select stores, they observed a 15% reduction in stockouts, leading to a full-scale implementation.
4. Adoption Phase
Objective: Formalize the relationship through integration, investment, or acquisition.
Options:
- Strategic Partnership: Collaborate on specific projects or initiatives.
- Equity Investment: Invest capital in exchange for ownership stakes.
- Joint Ventures: Establish a new entity jointly owned to pursue shared objectives.
- Acquisition: Fully acquire the startup to integrate its assets and talent.
Considerations:
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Ensure all agreements comply with relevant laws.
- Cultural Integration: Address differences in corporate culture to facilitate smooth integration.
- Ongoing Support: Provide resources, mentorship, and support to nurture the startup's growth.
Downloadable Resource: Access this Startup Scouting Process Template for detailed guidance through each phase.
For advanced techniques on market analysis to enhance your scouting, refer to Leveraging Market Insights for Startup Scouting.
Advanced Evaluation Criteria

Evaluating Startup Metrics
A thorough evaluation goes beyond basic metrics. Consider these advanced criteria:
Team Dynamics and Leadership Assessment
- Team Composition: Assess diversity in skills, backgrounds, and perspectives.
- Leadership Quality: Evaluate leaders' vision, adaptability, and ability to inspire.
- Team Cohesion: Observe how team members interact and collaborate.
- Cultural Considerations: Understand the startup's cultural values and how they align with yours, especially in global contexts. Factors include communication styles, work ethics, and decision-making processes.
Example:
When scouting an international fintech startup, consider how cultural norms in their home country might influence their business practices and customer interactions.
Market Potential and Scalability Analysis
- Total Addressable Market (TAM): Estimate the maximum revenue opportunity.
- Serviceable Available Market (SAM): Identify the segment of TAM targeted by the startup.
- Growth Projections: Analyze market trends and potential for expansion.
- Scalability Factors: Assess the startup's ability to handle growth in customers, operations, and geography.
Analytical Tools:
- Porter's Five Forces: Evaluate industry attractiveness.
- PESTEL Analysis: Examine Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors.
Technological Innovation and IP Considerations
- Innovation Level: Determine if the technology is incremental, disruptive, or radical.
- Intellectual Property Protection: Review patents, trademarks, and copyrights to safeguard innovations.
- R&D Capabilities: Assess ongoing commitment to research and development.
- Technology Roadmap: Understand future plans for technological advancements.
Key Questions:
- Does the startup have defensible technology?
- Are there any potential infringement risks?
Financial Health and Funding Requirements
- Revenue Streams: Assess diversification and sustainability of income sources.
- Profit Margins: Analyze gross and net margins indicating profitability.
- Cash Flow Management: Evaluate the ability to manage operational expenses and investments.
- Funding History: Review previous funding rounds, investors involved, and terms.
- Valuation Justification: Ensure alignment of valuation with market norms and company performance.
Financial Ratios to Consider:
- Burn Rate: Monthly expenditure rate.
- Runway: Time before current funds are exhausted.
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio: Measure of financial leverage.
Case Study:
Explore how an investment firm evaluated a biotech startup's financial viability, focusing on long R&D cycles and significant upfront costs. Read the Case Study on Evaluating Biotech Startups.
Dive deeper with our Guide to Evaluating Key Startup Metrics to enhance your assessment strategies.
Managing Networks and Collaboration
Building Diverse Networks
A strong and diverse network is crucial for effective startup scouting. Here are strategies to expand and leverage your connections:
Engaging with Incubators and Accelerators
- Partnership Agreements: Formalize relationships to access their startup cohorts.
- Mentorship Programs: Offer expertise to startups, positioning your organization as a valuable mentor.
- Co-host Events: Collaborate on workshops, seminars, or pitch sessions.
Benefits:
- Early access to high-potential startups.
- Insights into emerging trends and technologies.
- Opportunity to influence startup development.
Online Communities and Universities
- Academic Partnerships: Sponsor research projects or innovation labs at universities.
- Online Platforms: Participate in digital forums like Stack Exchange, GitHub communities, and industry-specific social media groups.
- Innovation Challenges: Host competitions to attract innovative solutions to specific problems.
Success Story:
A tech corporation partnered with a leading university, resulting in several startups that became key partners in AI development.
Personalization Techniques
- Industry Focus: Tailor scouting efforts to industries where your organization has expertise or strategic interest.
- Geographic Targeting: Focus on regions with vibrant startup ecosystems aligning with your market strategy.
- Customized Communication: Approach startups with personalized messages highlighting mutual benefits.
Actionable Tip:
Develop profiles for the types of startups you're interested in to refine your outreach and engagement strategies.
Use this Network Expansion Checklist to plan your outreach and build a diverse network effectively.
Tools and Software for Startup Scouting
What Tools Are Used for Startup Scouting?
Using the right tools enhances efficiency, depth, and accuracy in scouting activities. Here are categories of tools and examples:
Scouting Platforms
These platforms aggregate data on startups, investors, and industry trends.
Features to Look For:
- Detailed Profiles: Access to startup profiles with funding information and news updates.
- Search Filters: Ability to refine searches by industry, funding stage, location, and other criteria.
- Data Accuracy: Regularly updated and verified data.
- Integration Capabilities: Compatibility with CRM systems and analytics tools for seamless workflow.
AI and Data Analytics Tools
Artificial Intelligence and analytics software can process large datasets to identify patterns and insights.
Applications:
- Predictive Modeling: Forecast startup success probabilities.
- Trend Analysis: Identify emerging industries and technologies.
- Sentiment Analysis: Gauge market perceptions through social media and news sources.
Benefits:
- Automated Data Processing: Scan and analyze vast amounts of information quickly.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Use machine learning algorithms to inform investment decisions.
Process Management Software
These tools help manage workflows, collaborations, and data.
- Project Management Tools: Organize scouting activities with visual boards, lists, and cards to track progress.
- Collaboration Platforms: Assign tasks, set deadlines, and collaborate with team members on scouting projects.
- CRM Systems: Manage relationships and interactions with startups and partners.
Benefits:
- Centralized Information: Keep all scouting data accessible and organized.
- Task Automation: Set up reminders, notifications, and automated reports.
- Improved Collaboration: Enhance communication among team members and stakeholders.
Comparison Chart:
Review this Comparison of Top Startup Scouting Tools to select the best solutions for your needs, comparing features, pricing, and user reviews.
Challenges in Startup Scouting and Solutions
Common Pitfalls and Biases
Identifying and addressing challenges proactively improves the effectiveness of startup scouting.
Cognitive Biases
- Status Quo Bias: Preference for existing methods or solutions, hindering openness to new ideas.
- Halo Effect: Overemphasis on one positive attribute affecting overall assessment.
- Anchoring Bias: Relying too heavily on the first piece of information encountered.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Awareness Training: Educate teams about common biases and their impacts.
- Structured Decision-Making: Use quantitative methods and checklists to guide evaluations.
- External Perspectives: Involve third-party experts to provide unbiased opinions.
Over-Reliance on Trends
- Risk: Investing in overhyped sectors without thorough analysis can lead to poor outcomes.
- Solution: Focus on startups with solid fundamentals, regardless of current trends.
Example:
During the cryptocurrency boom, many investors backed blockchain startups without viable business models, resulting in significant losses when the market corrected.
Regulatory and Legal Considerations
Managing Global Regulations
- Varied Legal Landscapes: Different countries have unique laws governing investments, data privacy, and business operations.
- Compliance Requirements: Understand and adhere to regulations like GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California.
Strategies:
- Legal Expertise: Engage lawyers specialized in international business law.
- Due Diligence: Conduct thorough reviews of the startup's legal standing, licenses, and compliance history.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluate geopolitical risks and regulatory stability.
Protecting Intellectual Property
- Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs): Use NDAs to protect sensitive information during discussions.
- Intellectual Property Rights: Ensure the startup's IP is protected and there are no infringement issues.
Overcoming Information Overload
Effective Data Management
- Prioritization: Focus on key metrics aligned with your objectives.
- Data Visualization: Use dashboards and visual tools to interpret complex data.
- Automation: Employ AI tools to filter and analyze large datasets.
Productivity Tips:
- Set clear criteria for data relevance.
- Schedule regular data reviews to keep information current.
- Delegate data management tasks to specialized team members.
Checklist: Download this Risk Mitigation Checklist to address these challenges proactively and enhance your scouting process.
Future Trends Impacting Startup Scouting
Staying ahead of emerging trends ensures that your scouting efforts remain relevant and effective.
Impact of AI and Machine Learning
Enhancing Scouting Efficiency
- Automated Data Processing: AI can scan and analyze vast amounts of information quickly.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Machine learning algorithms can identify patterns and correlations that inform investment decisions.
- Virtual Assistants: Improve initial interactions and data collection from startups.
Action Points:
- Invest in AI tools tailored to your scouting needs.
- Train your team to interpret and utilize AI-generated insights.
- Stay informed about advances in AI technologies and applications in scouting.
Sustainability and Ethical Investment Trends

Focus on ESG Factors
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) considerations are increasingly influencing investment decisions.
- Environmental Impact: Assess startups' efforts in reducing carbon footprints and sustainable practices.
- Social Responsibility: Evaluate diversity, equity, and inclusion policies.
- Governance Standards: Review transparency in operations and honest business conduct.
Benefits:
- Aligns investments with societal values.
- Meets growing consumer and investor demands for responsible business practices.
- May offer long-term financial benefits as regulatory pressures increase.
Resources:
- ESG Rating Agencies: Use services to assess startups.
- Sustainability Reports: Review startups' disclosures on ESG initiatives.
Globalization and Cultural Considerations
Adapting to Diverse Markets
- Emerging Markets: Identify opportunities in regions with high growth potential but different cultural and business norms.
- Localization Strategies: Customize products and services to meet local preferences.
- Cross-Cultural Communication: Develop skills to navigate language barriers and cultural sensitivities.
Strategies:
- Hire local experts or partners to provide market insights.
- Conduct cultural training for your scouting team.
- Respect and understand local regulations and customs.
Case Study:
See how a capital firm successfully expanded into Southeast Asian markets by adapting scouting strategies to local cultural nuances and regulatory environments. Read the Full Case Study.
Strategies for Different Stakeholders
Recognizing and adapting to the unique needs of various stakeholders enhances the effectiveness of startup scouting. Here are strategies for different groups:
Corporate Innovation Managers
- Objective: Integrate startups into innovation strategies to drive organizational growth.
- Strategies:
- Prioritize startups offering solutions to existing organizational challenges.
- Establish internal innovation hubs to collaborate with startups.
- Align scouting efforts with long-term strategic plans.
Venture Capitalists and Investors
- Objective: Identify high-potential startups for investment and portfolio diversification.
- Strategies:
- Focus on startups with adaptable business models and strong market potential.
- Diversify investments across industries and stages.
- Use networks to access exclusive deals.
Startup Founders
- Objective: Understand what investors look for during scouting to attract investment.
- Strategies:
- Showcase unique value propositions and market differentiation.
- Build strong, diverse teams.
- Prepare comprehensive pitch decks highlighting key metrics.
Business Students and Academics
- Objective: Research startup ecosystems and scouting processes.
- Strategies:
- Analyze case studies of successful startup engagements.
- Study emerging trends and their impacts on the startup landscape.
- Participate in internships or projects with startups and investors.
For in-depth strategies tailored to specific stakeholders, read our Tailored Strategies for Effective Startup Scouting.
The Next Steps
Startup scouting is vital for organizations aiming to innovate, grow, and maintain a competitive edge in today's fast-paced business environment.
A strong understanding of the fundamentals, paired with strategic application, leads to effective navigation of the startup ecosystem and shared success.
Actionable Steps
- Implement a Structured Process: Follow the Discovery, Evaluation, Piloting, and Adoption phases for thorough scouting.
- Enhance Evaluation Techniques: Use advanced criteria and address cognitive biases for objective assessments.
- Use Technology: Incorporate AI and analytics tools to enhance efficiency and insights.
- Expand Your Network: Build relationships with diverse stakeholders in the startup ecosystem.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of future trends affecting startup scouting.
Apply the concepts and tools provided in this guide to enhance your scouting efforts.
For personalized guidance and expert support in your startup scouting journey, consider partnering with us. Our team offers tailored solutions to help you achieve your investment and innovation goals.
Discover more in our Comprehensive Startup Scouting Guide.
Key Takeaways
- Structured Scouting Process: Implement a methodical approach—Discovery, Evaluation, Piloting, Adoption—for effective scouting.
- Deep Evaluation: Assess startups beyond basic metrics, considering team dynamics, market potential, technological innovation, and financial health.
- Build and Use Networks: Engage with incubators, accelerators, online communities, and universities to expand your reach.
- Use Advanced Tools: Incorporate AI and data analytics tools to enhance efficiency and decision-making.
- Address Challenges Proactively: Tackle cognitive biases, regulatory hurdles, and information overload head-on.
- Stay Ahead of Future Trends: Adapt to trends like AI integration and ESG considerations to keep your scouting relevant.
- Customize Strategies: Tailor your scouting approach based on stakeholder needs and investment goals.
Frequently asked Questions
What Is Startup Scouting?
Startup scouting is the process of proactively identifying, evaluating, and engaging with startups that have the potential to drive innovation and provide strategic value to organizations. It involves searching for early-stage companies that align with specific objectives, assessing their potential, and building relationships that may lead to partnerships, investments, or acquisitions.


 Back
Back


